The purpose of magnetometry is to identify subsurface phenomena by measuring the magnetic field. Magnetometry incl
It is a geophysical method that has many applications in various fields.
Capable of air and sea withdrawals in addition to withdrawals
Ground, being cheaper than many other geophysical methods, the existence of relatively comprehensive software for data processing and interpretation, etc. has made this method one of the most widely used and cheapest geophysical methods.
This method is relatively old compared to
Other methods have caused more accurate tools to be made for this method and more specialists to use this method
As a result, many problems in the field of data processing and interpretation will be solved. The purpose of compiling this article is to give a brief introduction with a look at its many uses. This method is used in fields such as exploration of mineral deposits, oil exploration, identification
It is used in cavities and karsts, geology, environmental studies, archeology, identification of buried metal objects, etc.
- Exploration of mines
Magnetometry is a relatively low-cost, fast technique and one of the most widely used geophysical methods. This method is widely used in the search for metal deposits that are accompanied by iron
It is done with high speed and economically by airborne methods.
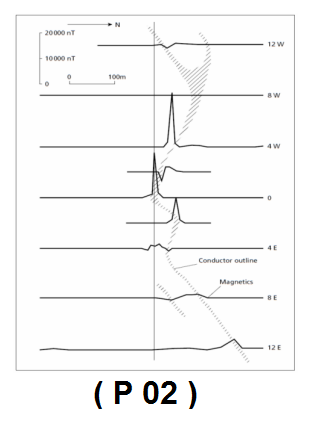
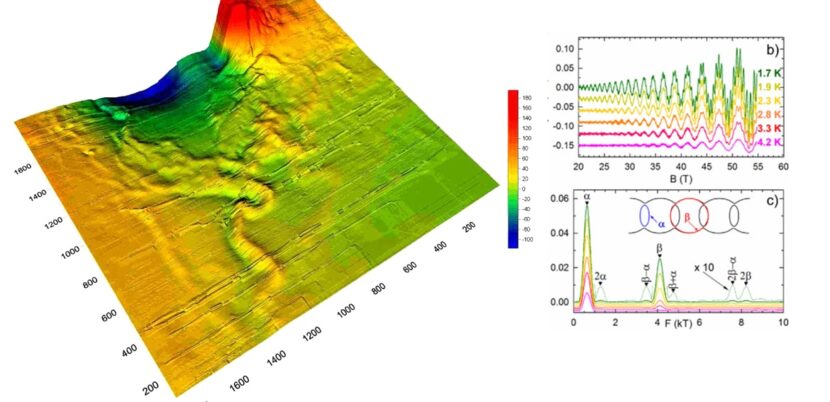
Magnetometry has a high capability in locating masiosulfide deposits, especially if it is combined with
Electromagnetic methods should be done (Figure No. 02).
The main and basic purpose of magnetometry is to find iron deposits
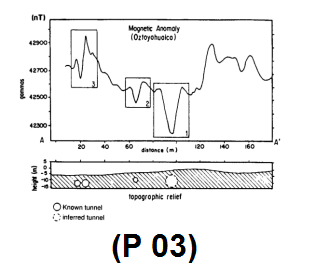
- Height and topography correction
The vertical gradient of the geomagnetic field is only about 1-km 03nT.0 in
Poles and 1-km 015nT.0- is at the equator, so correct the altitude
It is not usually done. The effect of topography in terrestrial magnetometry can be very large and important, but it cannot be predicted precisely because it depends on the magnetic properties of the effects of the topography of the earth; Therefore, topography correction is rarely done in terrestrial magnetometry
.
- Height and topography correction
The vertical gradient of the geomagnetic field is only about 1-km 03nT.0 in
Poles and 1-km 015nT.0- is at the equator, so correct the altitude
It is not usually done. The effect of topography in terrestrial magnetometry can be very large and important, but it cannot be predicted precisely because it depends on the magnetic properties of the effects of the topography of the earth; Therefore, topography correction is rarely done in terrestrial magnetometry.

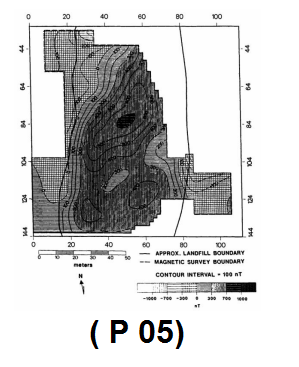
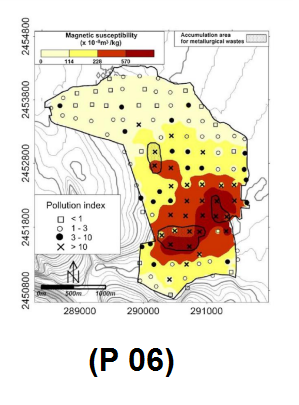
- Identification of buried metal objects
The primary goal of these studies is to identify buried metal objects such as pipes,
Wall pipes of water or oil wells that have been abandoned are landfills for municipal wastes, etc.
These buried objects are sometimes related to life issues
the environment is very important; For metal, sometimes buried waste contains toxic and dangerous substances. Mainly, the depth of study in this
The method is very little.
Geology
In academic studies, magnetometry is used to detect large-scale features of the continental crust over a wide area, although the source of the large and main magnetic anomalies is related to rocks of basic or ultrabasic composition. In addition, magnetic measurements are limited in studying the greater depths of the continental crust
Because the Curie isotherm for common ferromagnetic minerals at depth
It is located about 20 km, and as a result, the origin of the anomalies is limited to the upper part of the continental crust







Leave a Reply